
With the rapid development of network technology, information security has become a concern for businesses and individuals. Organizations increasingly need strong security measures. In this context, IPSec provides a set of protocols and mechanisms to encrypt, authenticate, and ensure the integrity of data packets.
In this article, we’ll take you deeper into the IPSec universe, where you’ll learn about its components, uses, and more.
What is IPSec
IP Security is a set of protocols designed to protect Internet Protocol (IP) communications by authenticating and encrypting each IP packet in the data stream. It establishes a structure for encrypting and authenticating packets transmitted over an IP network.
IPSec guarantees the confidentiality, integrity, and legitimacy of transmitted information. It facilitates secure communication between devices, even over potentially vulnerable networks such as the Internet.
What is the technical architecture of IPSec?
IPSec has three major subfields, as shown below. Technically, AH and ESP are the algorithms designed for IP Security, and IKE is a protocol used to exchange secret keys, which will be used for AH/ESP. So AH/ESP and IKE have slightly different functionality.
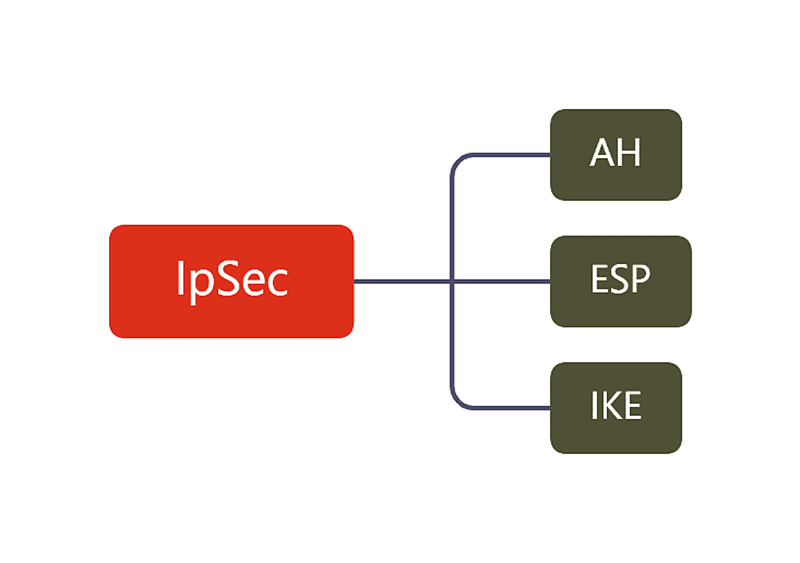
Authentication Header (AH)
The IPSec Authentication Header provides data integrity and source authentication, i.e., it ensures that the origin of transmitted IP messages is trusted and that the data is not tampered with, but it does not provide encryption.
The AH protocol adds an AH header to each packet’s standard IP header, and the scope of the AH protocol’s integrity check for the message is the entire IP message. The AH contains a symmetric key hash function that makes it impossible for third parties to modify the data in transit.
Encapsulating Security Payload (ESP)
IPSec Encapsulating Security Payload (ESP) provides data encryption; ESP utilizes a symmetric key to encrypt IP data (e.g., TCP packets) and supports the following encryption algorithms.
- DES-CBC (Data Encryption Standard Cipher Block Chaining Mode): 56-bit key.
- 3DES-CBC (Triple DES CBC): 56-bit key.
- AES128-CBC (Advanced Encryption Standard CBC): 128-bit key.
In transport mode, the IP header is not encrypted; only the IP data is encrypted.
Internet Key Exchange (IKE)
The IKE protocol is a UDP-based SA negotiation and critical management application layer. It is a hybrid protocol combining ISAKMP (Internet Security Association and Key Management Protocol), Oakley, and SKEME. These three protocols.
Among them, ISAKMP defines the establishment process of IKE SA, and the core of Oakley and SKEME protocols is the DH (Diffie-Hellman) algorithm, which is mainly used for distributing keys and verifying identities securely over the Internet to ensure the Security of data transmission. The encryption and authentication keys required by IKE SA and IPSec SA are generated through the DH algorithm. DH algorithm is generated, and it also supports dynamic key refreshment.
The IKE protocol is divided into two versions: IKEv1 and IKEv2. Compared with IKEv1, IKEv2 repairs several recognized security holes in cryptography improve security performance and simplifies the security alliance negotiation process to improve negotiation efficiency.
Core principles of IPSec
Internet Protocol Security is built on several core principles that ensure secure communications over IP networks. These principles are designed to protect data integrity, confidentiality, and availability, making IPSec a powerful solution for modern network security.
- Confidentiality: Ensuring that only those authorized to access the data can do so.
- Integrity: Maintaining the accuracy and integrity of data during transmission.
- Authentication: Confirms the identity of entities involved in a communication.
- Key Exchange: Securely exchanges encryption keys to enable encrypted communications.
How does IPSec work?
To know about how this works, you can go through the following points:
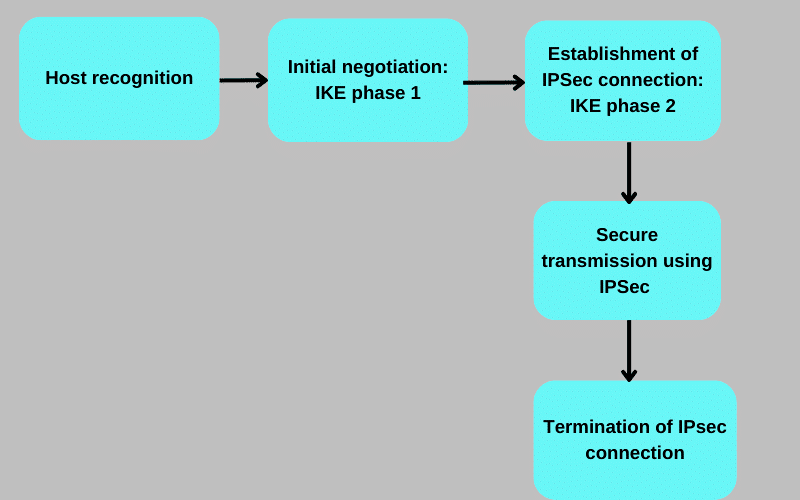
1. Host recognition
Before initiating any secure communication, IPsec-enabled devices must recognize each other. This recognition involves verifying the identity of the communicating hosts to ensure they are authorized to establish a secure connection.
2. Initial negotiation: IKE phase 1
The first phase of IKE involves negotiating a secure channel between the two devices. During this phase, they exchange encryption keys and establish a secure communication channel. This phase also ensures mutual authentication and sets the foundation for secure communication.
3. Establishment of IPSec connection: IKE phase 2
Once the secure channel is established, IKE phase 2 is initiated to negotiate the parameters of the IPsec SAs. This includes agreeing on encryption algorithms, integrity checks, and other Security parameters. Once completed, the devices have a secure tunnel to transmit data.
4. Secure transmission using IPSec
With the IPsec SAs in place, data packets are encrypted and authenticated before being transmitted over the network. ESP or AH Protocols protect the payload and ensure data integrity. They also provide a high level of security for the information transmitted.
5. Termination of IPsec connection
When the secure communication is no longer needed, the IPsec connection can be terminated. This occurs either through manual intervention or automatically based on predefined criteria.
Comparing IPSec with SSL/TLS
Comparing IP Security (IPSec) with SSL/TLS reveals key application and functional differences.
- Operating Layer: IPSec operates at the network layer and protects all IP traffic. In contrast, SSL/TLS operates at the transport layer and primarily protects Web traffic and other application layer protocols.
- Use Cases: IPSec is commonly used in VPNs to protect end-to-end IP communications, while SSL/TLS is widely used to protect Web transactions, e-mail, and other Internet-based communications.
Impact of IPSec on Network Performance
IP security (IPSec) can significantly impact network performance in various ways.
- Latency: Increased due to encryption and decryption processes.
- Throughput: This may be reduced due to additional processing.
- CPU utilization: higher because encryption tasks are computationally intensive.
Conclusion
In summary, Internet Protocol Security (IPSec) is a key technology for protecting IP communications. It ensures that data transmitted over IP networks remains confidential and secure. By understanding the various aspects of IPSec, Businesses can effectively protect their network communications
Read more