Fiber optic technology was originally developed for data center applications, and from the current development perspective, it will soon become an ideal choice for building backbone networks.
With the development and application of wireless technology, the horizontal cabling bandwidth in commercial and industrial buildings has exceeded 1 Gbps, and the consequent requirement is that the cabling backbone infrastructure supports at least 40 Gbps and 100 Gbps. This means that high-density application promotion in data centers is very suitable for current development and needs. OM5 fiber broadband can support not only 802.11ac wi-fi systems but also high-density 5G wireless networks.
Basic knowledge of high-density OM5 fiber
The ISO and TIA standardization organizations released the latest wiring standards ISO 11801 3rd and TIA-568.0-D in 2017 respectively.
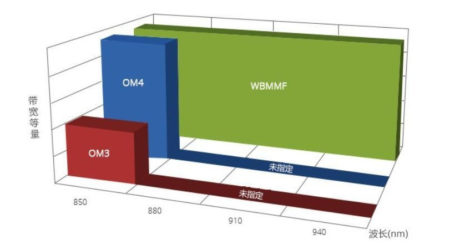
OM5 Broadband Multimode Cable: Attenuation has been reduced from 3.5 dB/km for previous OM3, OM4 cables to 3.0 dB/km, and increased bandwidth requirements at 953 nm. The geometry of the OM5 (50μm core, 125μm cladding) is identical to that of OM3 and OM4, so it can be backward compatible with these types of fibers.
OM5 fiber supports both future 400G Ethernet, for higher speed 400G Ethernet applications such as 400G Base-SR4.2 (4 pairs of fiber 2 wavelengths, 50G PAM4 per channel) or 400G Base-SR4.4 (4 For 4 wavelengths of fiber, 25GNRZ for each channel, only 8-core OM5 fiber is required. OM5 fiber is a laser-optimized multimode fiber (MMF) that specifies bandwidth characteristics for wavelength division multiplexing (WDM). The goal of this new fiber classification method is to support multiple “short” wavelengths between 850 nm and 950 nm, which are suitable for high bandwidth applications after polymerization.
What is the difference between the OM5 fiber cable and OM3/OM4 fiber cable?
1. Outer Sheath Color: Generally speaking, the outer sheath color of OM3 and OM4 fiber patch cords is cyan or purple, while the outer jacket color of OM5 fiber patch cords is water green.
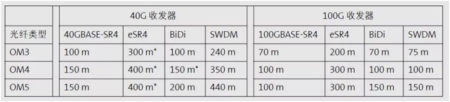
2. Wavelength: The OM5 fiber patch cord has an operating wavelength of 850/1300 nm and can support at least 4 wavelengths. The normal operating wavelengths of OM3 and OM4 are 850 nm and 1300 nm. In the same wavelength window, the transmission distance of this multimode fiber jumper is also different.
3. Effective Mode Bandwidth (EMB): The OM5 fiber patch cord has a higher breakthrough in effective mode bandwidth (EMB), which increases the effective mode bandwidth (EMB) at 850 nm to 6000 MHz.km, near the 880 nm wavelength. It is 8000MHZ.km, which is far superior to the traditional OM3 and OM4 multimode fiber patch cords.
What are the advantages of OM5 fiber cable?
High recognition: The OM5 fiber patch cord was originally released by the Communications Industry Association as TIA-492AAAE and was unanimously approved in the ANSI/TIA-568.3-D revision opinion issued by the American National Standards Institute;
High scalability: OM5 fiber patch cords can combine short-wavelength division multiplexing (SWDM) and parallel transmission technologies in the future, and only require 8-core wideband multimode fiber (WBMMF) to support 200/400G Ethernet. application;
Reduced costs: OM5 fiber patch cords draw on wavelength division multiplexing (WDM) technology for single-mode fiber, extending the available wavelength range for network transmission, enabling four wavelengths on a 1-core multimode fiber, and the required fiber core The number is reduced to 1/4 of the previous one, which greatly reduces the wiring cost of the network;
Compatibility and interoperability: OM5 fiber patch cords support legacy applications like OM3 fiber patch cords and OM4 fiber patch cords, and are fully compatible and interoperable with OM3 and OM4 fiber patch cords.
Transmission distance of OM5 fiber