
We often see the network cable, and the three common twisted pairs, coaxial cables, and optical cables are all network cables. The “network cable” we often say refers to the twisted pair. It is a data transmission line composed of many pairs of wires, which is characterized by the low price, so it is widely used. So why is it called a twisted pair? What kinds are there? What issues should we pay attention to when choosing a network cable? Let’s take a look at these issues.
The origin of the twisted pair name
Twisted pair, as the name implies, are twisted together by two wires, specifically a pair of mutually insulated metal wires. What is common in our actual use is that multiple pairs of twisted pairs are wrapped together in an insulated cable sleeve. Putting one or more pairs of twisted pairs in an insulating sleeve is generally called a twisted pair cable, but in daily life, it is generally referred to as a twisted pair.
Why is it necessary to take two wires together? The main reason is that in this way, the electric wave radiated by each wire in the transmission will be canceled by the electric wave emitted from the other wire, which can effectively reduce the signal interference. Degree.
Type of twisted pair cable
According to whether there is a shield classification
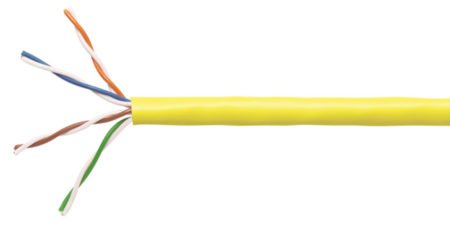
Unshielded twisted pair, picture source: CommScope
If you have a wide variety of twisted-pair cables, you will find that some twisted-pair cables have a metal shield between the twisted pair and the outer insulating jacket, and some do not. A metal shield is called a shielded twisted pair, and no one is called an unshielded twisted pair.
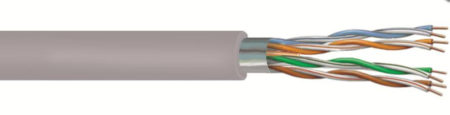
FTP twisted pair, picture source: CommScope
Shielded twisted pair is also divided into STP (Shielded Twisted Pair) and FTP (Foil Twisted-Pair). STP means that each line has its own shielding layer, and FTP only has a shielding device for the entire cable, and both ends are properly grounded. It only works. Therefore, the entire system is required to be a shielding device, including cables, information points, crystal heads, and distribution frames, and the building needs to have a good grounding system.
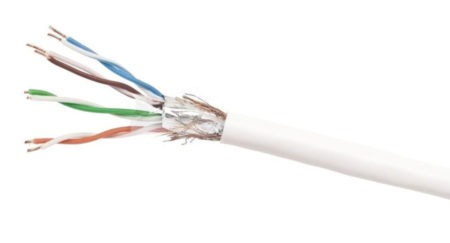
STP twisted pair, picture source: CommScope
The shielding layer has the advantages of reducing radiation, preventing information from being eavesdropped, and preventing external electromagnetic interference from entering so that the shielded twisted pair has a higher transmission rate than the similar unshielded twisted pair. However, in practical applications, in addition to the expensive price of the shielded twisted pair cable, it is even more uncomfortable than the installation and construction is extremely complicated. If the installation is not good, the shielding layer itself will become the biggest source of interference, resulting in even worse performance than unshielded twisted pair. So, usually, we see unshielded twisted pair.
Of course, in places with special needs, such as military, intelligence, embassy, and government departments such as the National Audit Office and the Ministry of Finance, shielded twisted pair cables can be used to effectively prevent external electromagnetic interference from line data. For sensitive instruments around the line, shielded twisted pairs can also be used to avoid interference.
Classification by internal strand
If you have been exposed to twisted-pair cables in the early years, you may see the twisted-pair cable stripping in the early years. There are only 4 cores, that is, 2 pairs of twisted pairs, because the maximum transmission rate is only 10Mbps. It has now been eliminated. Most of the current twisted pair cables are 8-core, that is, 4 pairs of twisted pairs, and in addition to the twisted pair cable that enters ordinary household users, there are also large logarithmic communication cables for outdoor use, generally 25 For the basic unit.

25 pairs of communication cable picture source: CommScope
Classified by frequency and signal to noise ratio
For the average person, according to the frequency and signal-to-noise ratio, it is the most familiar classification method. The “five types of lines”, “super five lines” and “six types of lines” that we often hear are based on frequency and signal noise. More than the classification. This is not introduced when it is too old to be eliminated. Let’s start with the five types of lines.
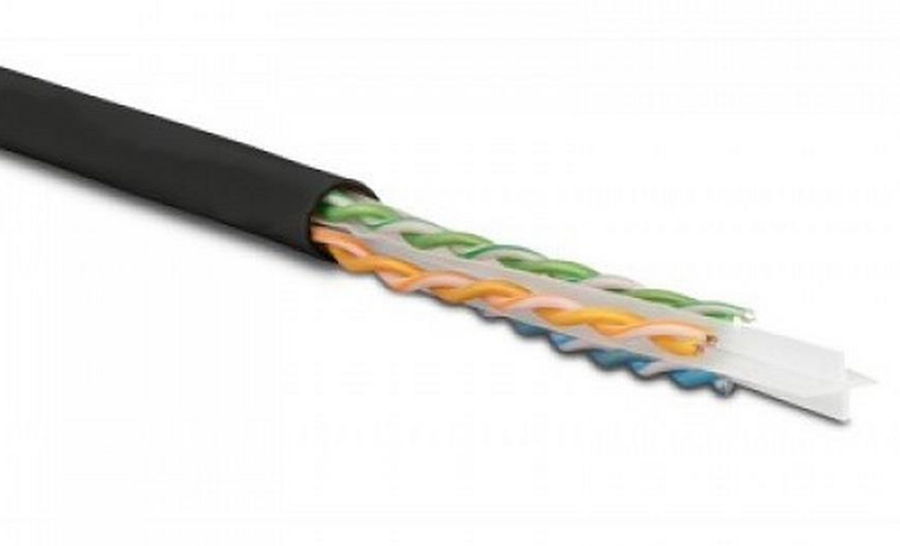
Category 5: The cable is labeled CAT5 and has a transmission frequency of 100MHz. It can be used for voice transmission and data transmission with a maximum transmission rate of 100Mbps. This is an Ethernet cable that is still common today.
Cat5e, picture source: CommScope
Super Category 5: The cable is labeled CAT5e. The Super Category 5 cable has the characteristics of low attenuation and low crosstalk and has higher attenuation and crosstalk ratio and signal to noise ratio and smaller delay error. Its transmission frequency is 100MHz, and the highest data transmission rate is 1000Mbps, which is greatly improved compared with the Category 5 line.
Category 6 line: The cable is labeled CAT6. The Category 6 line improves performance in terms of crosstalk and returns loss compared to the Category 5 line. Its maximum transmission frequency is 250MHz and the maximum data transmission rate is 1000Mbps. The six types of twisted pairs are different in appearance and structure from the five or five types of twisted pairs. They not only increase the insulated cross skeleton but also place the four pairs of twisted pairs on the cross skeleton. Within the grooves, and the diameter of the cable is also thicker.

Category 6A, picture source: CommScope
Super Category 6A: The cable is labeled CAT6A with a transmission frequency of 500MHz and a maximum data transmission rate of 10Gbps.
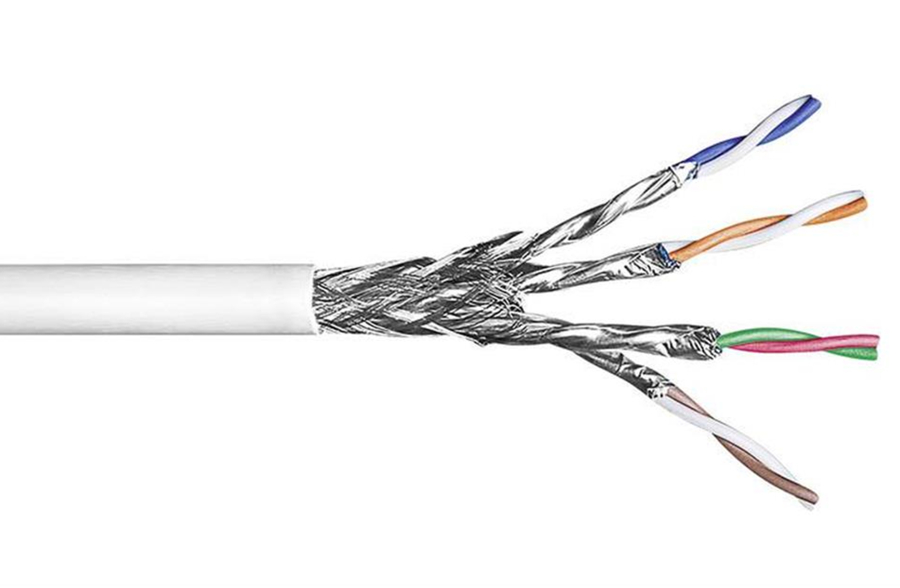
Cat7 cable, picture source: CommScope
Category 7 cable: The cable is labeled CAT7 with a transmission frequency of 600MHz and a maximum data transmission rate of 10Gbps.
Category 8 cable: The cable is labeled CAT8 with a transmission frequency of 2 GHz and a maximum data transmission rate of 40 Gbps.
About the choice of network cable
Due to the rapid development of information technology, the amount of data transmission has become larger and larger. In the home decoration wiring, it is necessary to consider the future trend. It is theoretically recommended to install the most advanced cable products to avoid insufficient bandwidth in the future. problem. Of course, if it is a bright line, it does not matter.
In addition, there is now a flat network cable on the market, the characteristics of the shape will not be said, talk about the inherent technical differences. In terms of structure, the inner cores of the flat mesh wires are straight lines and are opposite to each other; while the inside of the round mesh wires is mutually twisted, the anti-interference is stronger, and the signal can be transmitted far.
In the short-distance transmission, the transmission effect of the flat network cable and the circular network cable is not much different. Since the anti-interference ability of the flat cable is much smaller than that of the circular network cable, it is not suitable for long-distance transmission. The round table can be up to 95 meters long, while the flat wire is usually only a short jumper, up to 2 meters.