Fog Computing, the data in this mode, the (data) processing and application set on the edge of the network device, but not nearly all stored in the cloud is the cloud (Cloud Computing) extending the concept of the Cisco (Cisco) proposed. This name for “cloud” and “fog” comes from the phrase “fog is a cloud closer to the ground.”
Fog Computing is as vivid as cloud computing. The clouds float in the sky, high above, out of reach, deliberately abstract; and fog is realistic, close to the ground, right next to you and me. Fog Computing is not made up of powerful servers but is composed of functional computers with weaker performance and more dispersion. They are infiltrated into factories, automobiles, electrical appliances, street lamps and various materials in people’s material life.
Concept
The concept of fog computing was proposed in 2011 and was defined in detail in 2012. Just like cloud computing, fog computers are also very well defined. The clouds are high in the sky, very abstract, and the fog is close to the ground, with you and me. Fog computing has no powerful computing power, only a few weak, scattered computing devices.
Fog computing, the name was initiated by Professor Stern Buddha of Columbia University in New York, USA. His purpose was to use “fog” to stop hacking. Cisco first proposed it, giving the fog a new meaning. Fog computing is a distributed computing infrastructure for the Internet of Things that extends computing power and data analytics applications to the “edge” of the network, enabling customers to analyze and manage data locally for instant insights through connectivity.
Characteristics
Fog computing is an extension of the concept of cloud computing. The cloud computing weaknesses described above are not available in fog computing. In addition, it mainly uses devices in the edge network, and data transfer has extremely low latency. Fog computing has a vast geographical distribution, a large-scale sensor network with a large number of network nodes. The fog computing mobility is good, the mobile phone and other mobile devices can communicate directly with each other, and the signal does not have to go to the cloud or even the base station to circle, supporting high mobility.
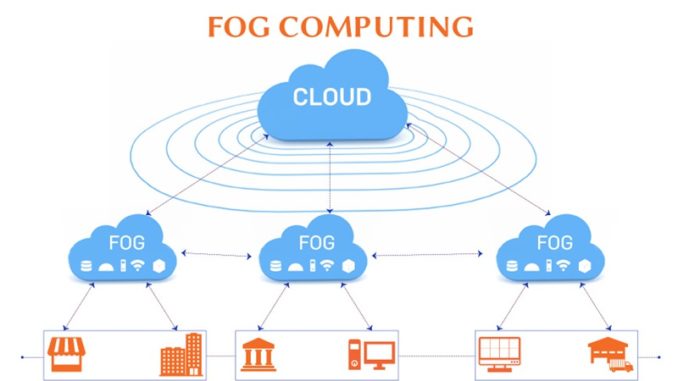
Fog computing is not a powerful server, but a weaker and more distributed computer. The fog computing is between cloud computing and personal computing. It is a paravirtualized service computing architecture model. Emphasize the number, regardless of how weak a single compute node is. Compared with cloud computing, the architecture of fog computing is more distributed and closer to the edge of the network.
Fog computing centralizes data, data processing, and applications at the edge of the network, rather than storing them almost entirely in the cloud like cloud computing. Data storage and processing rely more on local devices than servers. Fog computing is a new generation of distributed computing, in line with the “decentralization” of the Internet. Since Cisco proposed fog computing, several major technology companies such as the ARM, Dell, Intel, and Microsoft, as well as Princeton University, have joined the concept camp and established a non-profit organization Open Fog Alliance to promote and accelerate the open fog computing. Popularize and promote the development of the Internet of Things. The fog computing is based on small clouds such as personal clouds, private clouds, and enterprise clouds.
Fog computing is completely different from cloud computing. Cloud computing is based on IT operator services and social public clouds. The fog computing wins by quantity, emphasizing the quantity, no matter how weak the ability of a single computing node is to play a role. Cloud computing emphasizes overall computing power and is typically calculated by a cluster of centralized high-performance computing devices. Fog computing expands the network computing model of cloud computing, extending network computing from the network center to the edge of the network, and thus more widely used in various services. Fog computing has several distinct features: low latency and position sensing, a wider geographical distribution, mobility-adapted applications, and support for more edge nodes. These features make mobile service deployment more convenient and meet a wider range of node access.
Application
The country is vigorously developing the Internet of Things. The ultimate result of the development of the Internet of Things is to interconnect all electronic devices, mobile terminals, household appliances, etc., which are not only large but also widely distributed. Only fog computing can be satisfied. Demand puts forward requirements for fog computing and also provides opportunities for the development of fog computing.
With fog computing, many businesses can be deployed. For example car networking. The application and deployment of the Internet of Vehicles require a rich connection and interaction. Car to car, car to access point ( wireless network, 3G, LTE, smart traffic lights, the navigation satellite network, etc.), access point to access point. Fog computing can provide information entertainment, security, traffic protection, and other services in the service menu of the Internet of Vehicles. Intelligent traffic lights in particular need to calculate the mobility and position information, the computing is not large, and the anti-delay requirement is high. Obviously, only the fog computing is most suitable. Imagine if all the traffic lights in the city need to have data center cloud computing to calculate and direct all traffic lights, which is not only timely and error-prone. The intelligent traffic light is designed to automatically direct the traffic according to the traffic flow. When the car is not in the red light, it is necessary to stop and wait until the green light goes. The real-time computing is very important, so each traffic light has its own computing power, so it can complete itself. Intelligent command, this is the power of fog computing.
The difference between cloud computing
Compared with cloud computing, the architecture of fog computing is more distributed and closer to the edge of the network. Fog computing centralizes data, data processing, and applications on devices at the edge of the network, rather than keeping them almost entirely in the cloud like cloud computing. The storage and processing of data depend more on the local device than on the server. Therefore, cloud computing is a new generation of centralized computing, and fog computing is a new generation of distributed computing, in line with the “decentralization” of the Internet.
Unlike cloud computing, fog computing requires users to connect to large remote data centers to access services. In addition to the architectural differences, the cloud computing can provide the application of cloud computing, but the computing platform used in fog computing may not be as efficient as the large data center.
Cloud computing carries the high hopes of the industry. It has been widely believed in the industry that future computing functions will be completely in the cloud. However, importing and exporting data from the cloud is actually more complicated and difficult than people think. As more and more access devices (especially mobile devices), bandwidth is stretched when transmitting data and getting information. With the rapid development of the Internet of Things and the mobile Internet, people are increasingly relying on cloud computing, more and more networked devices, devices are becoming more and more intelligent, mobile applications become the main way people handle transactions on the network, the amount of data and the number of data nodes Increasingly, not only will it take up a lot of network bandwidth, but it will also increase the burden on the data center, and data transmission and information acquisition will become worse and worse.
Therefore, with the distributed fog computing, the data transmission belt is formed between different devices through devices and technical means such as intelligent routers, which can effectively reduce the network traffic, and the computing load of the data center is correspondingly reduced. The fog computing can be used as a computational process between the M2M (machine-machine dialogue) network and the cloud computing to cope with the large amount of data generated by the M2M network – the processing program is used to pre-process the data to enhance its use value.
Fog computing can not only solve the problem of automation of networked devices but more importantly, it requires less data transmission. Fog computing, a technology that promotes the internal operation of cloud data centers, is conducive to improving local storage and computing capabilities and eliminating bottlenecks in data storage and data transmission.